Creating and Managing Asymmetric Keys
There are two ways to create asymmetric keys:
-
Create key in KeyControl Vault and open in Microsoft SQL Server
-
Create key directly in Microsoft SQL Server using SQL script
Create Asymmetric Key in KeyControl Vault
To configure the asymmetric key in KeyControl Vault.
-
Navigate to CLOUD KEYS > CloudKeys tab. Create the Key that will be opened in SQL server.
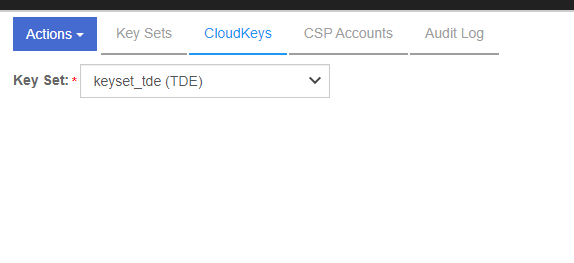
-
From the Action menu, select Create CloudKey.
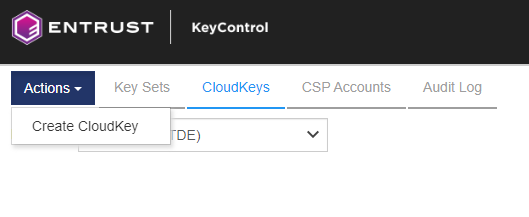
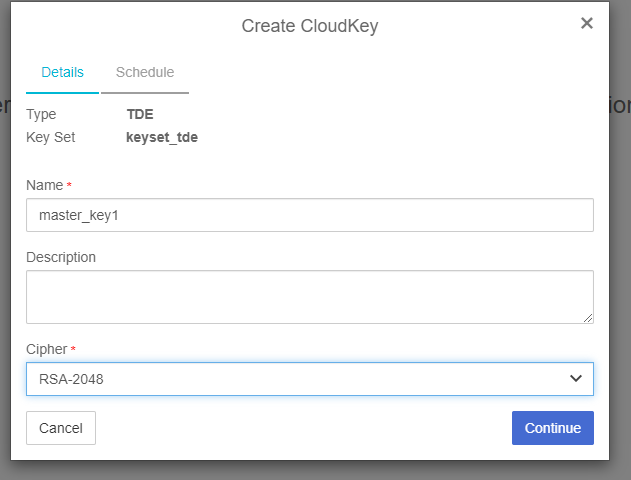
-
Check if the key is created properly by clicking the <key name> in the CloudKeys list. The key status must be "AVAILABLE".
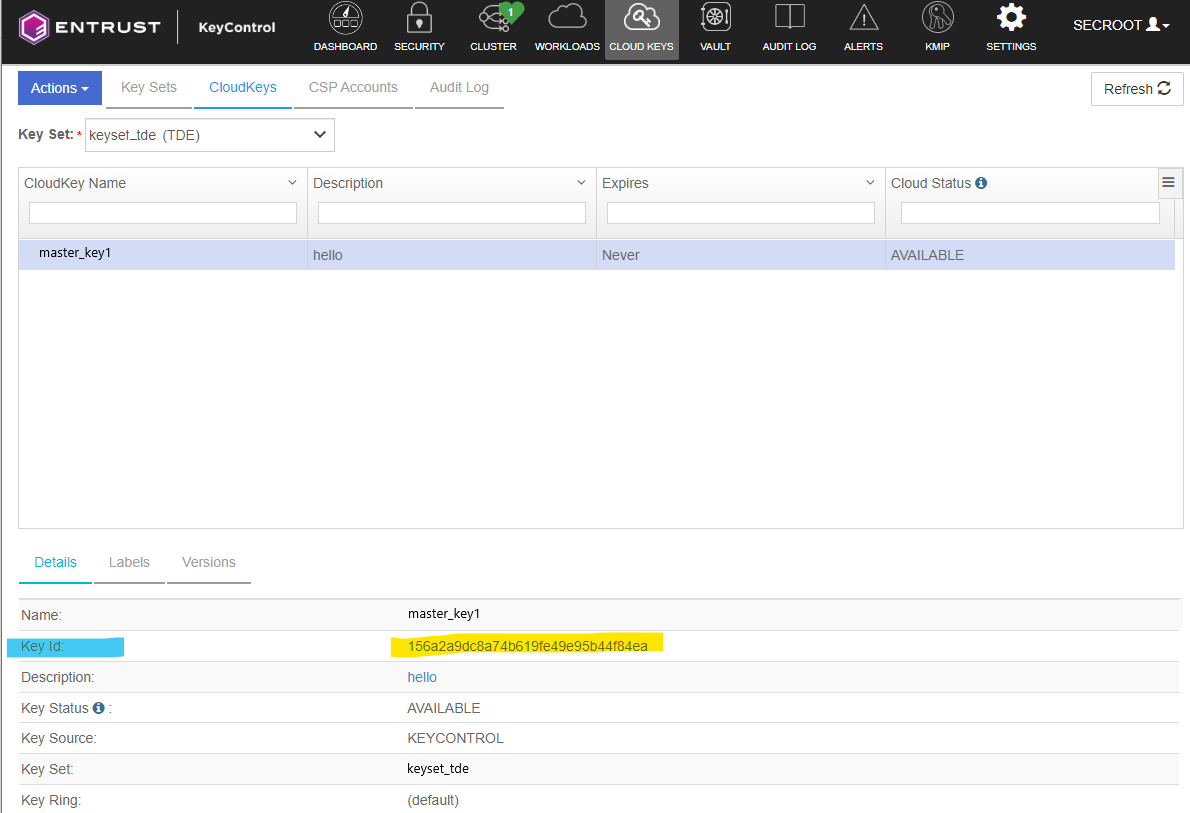
-
To import the asymmetric key in SQL Server.
CopyUSE <database name>
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY <key name in database>
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='<key name in provider>',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
GO
Creating asymmetric key using Microsoft SQL Server
To generate a new asymmetric key through the KeyControl Vault SQLEKM provider:
USE TestDatabase
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY dbRSA2048Key FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='ekmRSA2048Key',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = CREATE_NEW, ALGORITHM=<asymmetric algorithm>;
GOWhere
-
<provider name> is the name that is used to refer to the KeyControl Vault SQLEKM provider.
-
<asymmetric algorithm> is a valid asymmetric key algorithm descriptor.
Please note that there is a length restriction on this name of 31 characters maximum if created using a T-SQL query.
This example names the key `dbRSA2048Key` in the database, and `ekmRSA2048Key` in the KeyControl Vault.
Note: `IDENTITY_VALUE` is not a supported argument for asymmetric key generation.
Listing asymmetric keys in a database
To list the asymmetric keys in a database using SQL Server Management Studio:
-
Go to Databases > TestDatabase > Security > Asymmetric Keys. Right-click to select Refresh.
Alternatively, you may check keys by following the methods shown in Creating and Managing Asymmetric Keys .
Removing an asymmetric key from the database only
To remove the asymmetric key `dbRSA2048Key` from the database only (`TestDatabase`):
USE TestDatabase
DROP ASYMMETRIC KEY dbRSA2048Key;
GOAfter the above query completes, the key `dbRSA2048Key` is deleted from the database, but the corresponding key `ekmRSA2048Key` remains protected by the KeyControl Vault.
Re-importing an asymmetric key
To re-import a deleted asymmetric key (`dbRSA2048Key`) back into the database (`TestDatabase`), where a corresponding copy (`ekmRSA2048Key`) exists in the KeyControl Vault:
USE TestDatabase
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY dbRSA2048Key
FROM PROVIDER <provider name> WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='ekmRSA2048Key',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
GORemoving an asymmetric key from the database and provider
To remove the asymmetric key (`dbAES256Key`) from both the database (`TestDatabase`) and the KeyControl Vault, execute the following query:
USE TestDatabase
DROP ASYMMETRIC KEY dbRSA2048Key REMOVE PROVIDER KEY;
GOUsing this method means you do not have to name the corresponding key in the KeyControl Vault to remove it from there.
Important: Refer to your security policies before considering deleting a key from the KeyControl Vault. You cannot import a key into the database once you have deleted that key from the provider.
Creating a symmetric wrapped key from an asymmetric wrapping key
To create a symmetric wrapped key (`dbSymWrappedKey1`) from an asymmetric wrapping key (`dbAsymWrappingKey1`), execute the following query:
USE TestDatabase
CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY dbAsymWrappingKey1
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='ekmAsymWrappingKey1',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = CREATE_NEW, ALGORITHM=RSA_2048;
GO
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY dbSymWrappedKey1
WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256,
IDENTITY_VALUE ='yr7s365$dfFJ901'
ENCRYPTION BY ASYMMETRIC KEY dbAsymWrappingKey1;
GOWhere <provider name> is the name that is used to refer to the KeyControl Vault SQLEKM provider.
Note: If you wish to delete the wrapped and wrapping keys, you will have to delete the wrapped key first.
