Creating and Managing Symmetric Keys
Symmetric key GUIDs
When a new symmetric key is generated through the KeyControl, it is associated in the database with a Global Unique Identifier or GUID. The database issues a different and random GUID for every new key, and uses the GUID to identify the correct symmetric key for encryption or decryption purposes. As long as a copy of this key with the same GUID remains available to the database, it can be used indefinitely.
If the key is lost to the database, then a cryptographically equivalent duplicate can be generated through the KeyControl SQLEKM provider from the copy stored in the HSM. The duplicate key, although cryptographically identical to the lost key, will be issued with a new GUID by the database. Because the GUID is different from the original key it will not be identified with the original key, and will not be allowed to perform encryption or decryption of the data with which the lost key was associated.
To avoid this issue, you should always specify an `IDENTITY_VALUE` when generating a symmetric key. `IDENTITY_VALUE` is used to generate the key GUID in the database. The examples below create a symmetric key in the KeyControl SQLEKM provider, and make available the same key for use in the database. The key does not have to share the same name between the KeyControl SQLEKM provider and database.
There are two ways to create TDE keys:
-
Create key in KeyControl and open in Microsoft SQL Server
-
Create key directly in Microsoft SQL Server using SQL script
Create symmetric Key in KeyControl
To configure the TDE key in KeyControl.
-
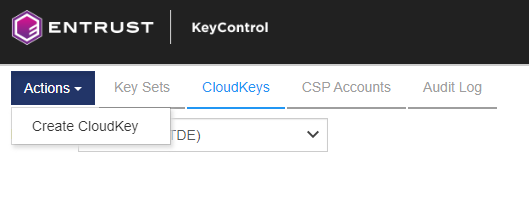
Navigate to CLOUD KEYS and select the CloudKeys tab. From the Key Set drop down menu, select the required Key Set.

-
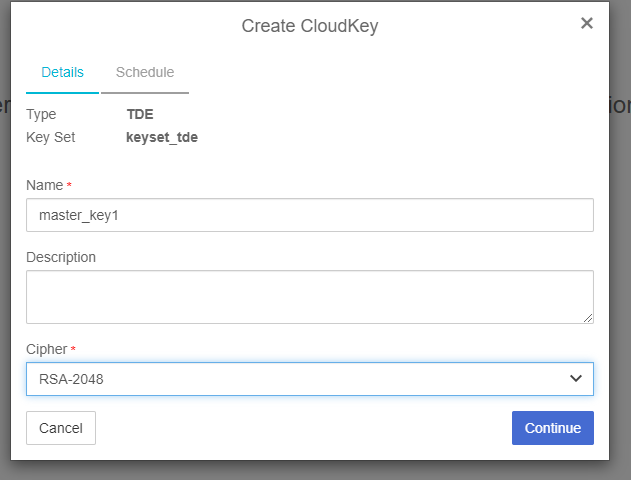
Select Action > Create CloudKey.
-
Check the key is created correctly. Select the <key name> in the CloudKeys list. The key status must be "AVAILABLE".

-
To import the key in SQL Server.
CopyUSE <database name>
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY <key name in database>
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='<key name in provider>',
IDENTITY_VALUE='<unique GUID generator string>',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
GONote: Note: The PROVIDER_KEY_NAME must be the name of the key given in the previous step.
Create symmetric key using Microsoft SQL Server
To create a symmetric key with an identity value:
USE <database name>
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY <key name in database>
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='<key name in provider>',
IDENTITY_VALUE='<unique GUID generator string>',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = CREATE_NEW, ALGORITHM=<symmetric algorithm>;
GOWhere:
-
<database name> is the name of the database for which you wish to provide encryption. See T-SQL Shortcuts and Tips for examples.
-
<provider name> is the name of the provider you are using.
-
<key name in database> is the name you wish to give the key in the database.
-
<key name in provider> is the name you wish to give the key in the provider. Note that there is a length restriction on this name of 31 characters maximum if created using a T-SQL query.
-
<unique GUID generator string> is a unique string that will be used to generate the GUID.
-
<symmetric algorithm> is a valid symmetric key algorithm descriptor.
Note: If the value of the <unique GUID generator string> is known to an attacker, this will help them reproduce the symmetric key. Therefore, it should always be kept secret and stored in a secure place. We recommend the <unique GUID generator string> shares qualities similar to a strong passphrase. Check your organization's security policy.
Only one key that has been created using a particular `IDENTITY_VALUE` can exist at the same time in the same database.
Creating a duplicate key
This example shows how a duplicate of a lost symmetric key can be made through the KeyControl SQLEKM provider and imported into the database.
To create a duplicate key:
USE <database name>
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY <key name in database>
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='<key name in provider>',
IDENTITY_VALUE='<unique GUID generator string>',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
GOWhere <unique GUID generator string> is the same value as used to create the original key.
Example
This query generates a new symmetric key through the KeyControl SQLEKM provider:
USE TestDatabase
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY dbAES256Key
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='ekmAES256Key',
IDENTITY_VALUE='Rg7n*9mnf29xl4',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = CREATE_NEW, ALGORITHM=AES_256;
GOIn this example, the key is named `dbAES256Key` in the database and `ekmAES256Key` in the KeyControl.
Listing symmetric keys in a database
To list the symmetric keys in a database using SQL Server Management Studio:
-
Go to Databases > TestDatabase > Security > Symmetric Keys (right-click to select Refresh).
Alternatively, you can use the following T-SQL script.
Check the key is created and has correct key thumbprint.
CopyUSE master;
select name,key_thumbprint,algorithm_desc from sys.symmetric_keys
GO
Removing symmetric keys from the database only
To remove the symmetric key `dbAES256Key` from the database only (`TestDatabase`):
USE TestDatabase
DROP SYMMETRIC KEY dbAES256Key;
GOAfter the above query completes, the key `dbAES256Key` is deleted from the database, but the corresponding key `ekmAES256Key` remains protected by the KeyControl .
Re-importing symmetric keys
To re-import the symmetric key (`dbAES256Key`) that was removed from the database, where a corresponding copy (`ekmAES256Key`) exists in the KeyControl:
USE TestDatabase
CREATE SYMMETRIC KEY dbAES256Key
FROM PROVIDER <provider name>
WITH PROVIDER_KEY_NAME='ekmAES256Key',
IDENTITY_VALUE='Rg7n*9mnf29xl4',
CREATION_DISPOSITION = OPEN_EXISTING;
GOThis example uses the same `IDENTITY_VALUE` as in the original key generation. This regenerates the same GUID. Having the same GUID means that the key is logically identical to the key it replaces.
Removing symmetric keys from the database and provider
To remove a symmetric key (`dbAES256Key`) from both the database (`TestDatabase`) and the KeyControl, execute the following query:
USE TestDatabase
DROP SYMMETRIC KEY dbAES256Key REMOVE PROVIDER KEY;
GOUsing this method means you do not have to name the corresponding key in the KeyControl to remove it from there.
Important: Refer to your security policies before considering deleting a key from the KeyControl. You cannot import a key into the database once you have deleted that key from the provider.
